In today’s competitive marketing landscape, brands are constantly evaluating the best ways to build long-term awareness and customer loyalty. Among the most debated strategies are print ads and native advertising—each with its strengths and weaknesses. However, as consumer behavior continues to evolve, a more personalized and effective alternative has emerged: in-hands advertising. In this blog, we’ll explore the long-term value of print and native advertising, compare their cost-effectiveness, and demonstrate why in-hands advertising presents a superior opportunity for brands seeking meaningful engagement.
Understanding Print Advertising vs. Native Advertising
Before diving into the cost-benefit analysis, let’s briefly define the two approaches:
Print Advertising
Print advertising involves placing ads in newspapers, magazines, brochures, and other physical media. It offers tangible and trusted brand visibility, often targeting specific demographics through well-established publications. Despite its credibility, print ads come with high production and placement costs, and their effectiveness is challenging to measure accurately.
Pros of Print Advertising:
High credibility and trust among older demographics.
Longer shelf life in magazines and newspapers.
Targeted reach through niche publications.
Cons of Print Advertising:
High costs for production and distribution.
Limited engagement tracking and measurability.
Declining readership due to digital media growth.
Native Advertising
Native advertising, on the other hand, integrates brand messages seamlessly within digital content, such as blogs, news websites, and social media. The goal is to offer value-driven, non-disruptive content that aligns with the platform’s tone and style.
Pros of Native Advertising:
High engagement due to non-intrusive nature.
Advanced tracking capabilities via analytics.
Greater potential for virality and shareability.
Cons of Native Advertising:
Can be perceived as deceptive if not properly disclosed.
Audience fatigue from overexposure to digital content.
Costs can rise over time with paid placements.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Print vs. Native Advertising
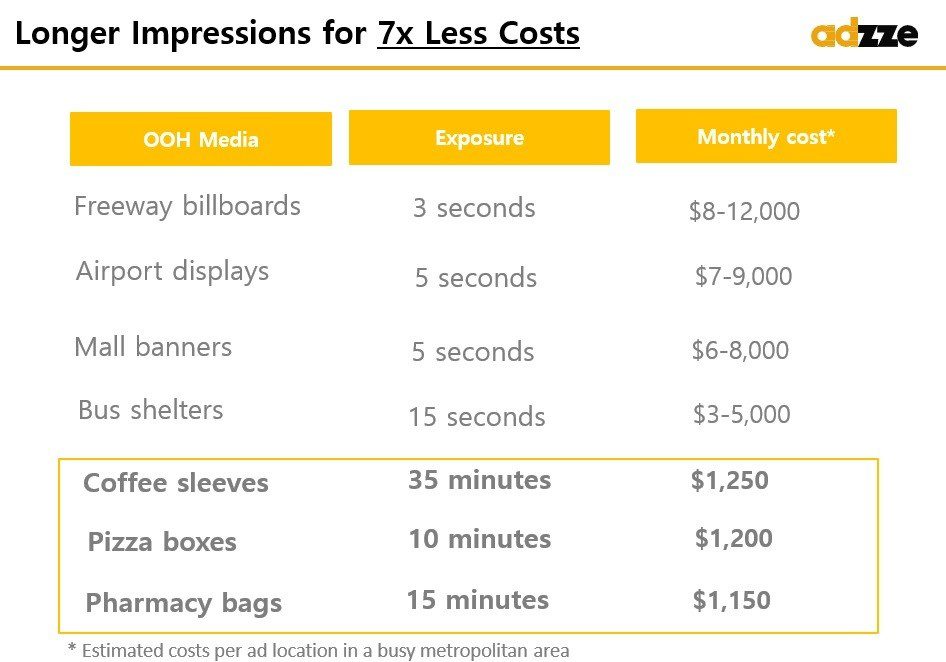
When comparing the cost-effectiveness of print vs. native advertising, several factors come into play, including reach, impressions, cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), and return on investment (ROI).
Reach and Impressions
Print ads are often limited to specific regions and readership, offering a fixed number of impressions based on circulation. A full-page ad in a major magazine may cost anywhere from $10,000 to $250,000, with estimated reach in the millions, but actual engagement rates are often lower.
In contrast, native advertising offers scalable reach, allowing brands to tap into diverse digital audiences. A sponsored article on a leading publication can generate hundreds of thousands of impressions, but the effectiveness largely depends on targeting and content relevance.
Key Insight: While native advertising may offer higher initial impressions, the quality and longevity of engagement in print media can sometimes yield better brand retention.